Choosing the Best RAID Configuration for Enterprise: RAID 10 vs. RAID 5
Summary: Selecting the perfect data storage solution can be tricky for B2B setups. RAID 5 emphasizes storage space and can handle one drive failure, while RAID 10 focuses on data security and high performance, making it great for B2B applications. Plus, RAID 10 can withstand multiple accidents, ensuring uninterrupted business operations. Let’s explore the difference between RAID 10 Vs RAID 5.
What is RAID 10?
RAID 10, also known as RAID 0+1 or mirrored striping, combines the two concepts. This includes striping & mirroring. In striping, the data is distributed across multiple disks in strips. Thus, this disk provides improved reading performance.
However, the failure of one drive can result in a permanent loss of data. This drive addresses this issue using mirror data on both drives. If one drive fails, a mirrored copy on the other drive ensures that the data is intact.
This storage type takes the best of both worlds. It removes data on mirrored pairs of drives, improving read performance with the added benefit of redundancy. Even if one drive in the mirrored pair fails, the controller can access data from the healthy drive in the pair.
This redundancy allows this disk to survive multiple drive failures without data loss, making it ideal for mission-critical applications where data integrity is important.
What is RAID 5?
RAID 5 uses a technique called distributed parity. The data is patched across all drives in the array, with parity information calculated from the data itself. This parity information enables the controller to reconstruct data in the event of a drive failure.
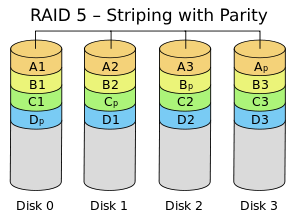
Unlike RAID 10, it doesn’t mirror data. Although this drive offers redundancy & improved storage efficiency compared to RAID 10. Hence, this storage type has its limitations.
Rebuilding an array after a failed drive can be a time-consuming process, & the system is vulnerable if a second drive fails during rebuilding. This weakness makes it less suitable for applications that require the highest data availability.
Additional Reading: Recover Data from Raid 5
Configuration of RAID 10 & RAID 5
For a RAID 10 configuration, you will need at least four disks. These discs are divided into pairs of crystals. Data is then transferred to these two mirrors, providing redundancy & improved performance.
For example, if you have a four-disk system, you have two pairs of mirrors, two disks each. The data in these pairs will be patched, to ensure redundancy & faster read speed.
RAID 5 requires a minimum of three disks. The data & parity information is distributed to all the drives in the array. While this drive offers some redundancy & efficient storage capacity usage, it does not offer the same data protection as RAID 10. Next, we will examine the raid level 10 vs 5 comparison.
Additional Reading: Raid Server Data Recovery Service
Difference Between RAID 5 & RAID 10
Here is the simple table comparing RAID 5 and 10 across various features:
| Feature | RAID 5 | RAID 10 |
|---|---|---|
| Data Distribution | Distributed with parity information | Mirrored pairs with striped distribution |
| Emphasis | Storage efficiency | Data security & performance |
| Reliability | Can withstand single drive failure | Better fault tolerance |
| Minimum Disk Number | 3 Disks minimum | 4 Disks minimum |
| Read Speeds | Generally perform well | Generally perform well |
| Write Speeds | Slightly slower | Faster |
| Preservation of Resources | Maximizes usable storage space | Reduced usable space due to mirroring |
| Redundancy & Fault Tolerance | Basic redundancy | Better fault tolerance |
| Complexity | Less complex configuration | More complex configuration |
| Cost | Inexpensive to implement | More expensive to implement |
| Composition | Data & parity distributed across disks | Mirrored pairs with striped distribution |
| Advantages | Storage efficiency, reduced risk during rebuild | Data security, performance |
| NAS Suitability | Supported by most NAS Devices. | May not work on all NAS devices |
With different RAID levels available, choosing the right one for your needs can be confusing. This guide dives deeper into the differences between raid 5 vs raid 10 performance, helping you choose the best storage saver.
1. Data Distribution
Suppose data is sliced into pieces of the stated size. RAID 5 distributes these blocks & some extra parity information to all the disks in the array. This parity allows the system to reconstruct lost data if one drive fails. Imagine having a recipe to add where memory can be used to recreate lost ingredients.
In RAID 10, data takes a different route. It’s first mirrored across pairs of disks. This drive creates an exact copy. Then, these mirrored pairs are striped, meaning data is distributed across them in stripes. You can say that it’s similar to having two recipe books with the same information. Hence, it is further divided into sections for easier access.
2. Emphasis
Storage efficiency is RAID 5’s strength. Maximizes storage capacity by using all available disk space. Consider using every nook and cranny of the pantry to store food properly.
RAID 10 prioritizes data security & performance. A mirrored setup ensures that data remains intact even after a drive failure, while striping provides faster access, just like a nice & easily accessible repository with built-in backup replicas.
3. Reliability
RAID 5 can withstand a single drive failure. Parity information helps rebuild lost data from the rest of the drive. However, in this architecture, the system is simple. If the second drive fails before the rebuild is complete, there is a possibility of data loss. Imagine breaking a jar of contents in the pantry. You can repeat with the leftovers, but another broken bottle before you’re done can result in lost ingredients.
RAID 10 provides better fault tolerance. Even if multiple drives fail in mirrored pairs, they can recover data. Each pair of lenses acts as an independent unit, so a failure in one does not affect the others. Similar to having several well-stocked backup pantries that continue to work even if a few pots break in the main.
4. Minimum disk number
RAID 5 requires a minimum of three disks. One disk stores the parity information, while the other two contain the data tracks.
RAID 10 requires a minimum of four disks. These are divided into pairs of crystals, and each pair is then taped for data distribution.
5. Read Speeds
Let’s do a raid 5 vs raid 10 speed test. Both systems generally perform well in reading speed tests. Backing up data on multiple disks allows for faster access compared to a single drive.
6. Write Speeds
Raid 5 vs raid 10 write speed is also an important consideration. Write speeds can be slightly slower in RAID 5 compared to RAID 10. This is because data writes require shared data bands & parity information to be exchanged across all disks
Write speeds in RAID 10 are faster because data is mirrored on two disks; writing requires updating both images in the two mirrors, simplifying the process.
7. Preservation of resources
Now, we have a raid 5 vs raid 10 performance comparison. It is time to compare the storage performance of these disks. RAID 5 for storage efficiency. Because this drive only uses one disk for parity information. Thus, maximizes usable storage space in the remaining disks.
RAID 10 loses some storage capacity due to mirroring. Half of the available disks are used for imaging, effectively reducing usable space. Imagine a warehouse where half of the shelves are dedicated to backup replicas.
8. Redundancy & fault tolerance
After raid 5 vs raid 10 storage you should check support for redundancy. RAID 5 provides basic redundancy withstanding drive failures. However, the architecture is a weakness.
RAID 10 provides better fault tolerance. This disk can survive multiple drive failures in mirror pairs, ensuring data recovery.
9. Complexity
RAID 5 provides flexible configuration. Data & parity issues are distributed across all disks, requiring less configuration compared to RAID 10.
RAID 10 requires a lot of configuration. Mirroring data on two disks adds another layer of complexity to the system design. Although additional effort is needed, the benefit is a higher level of data security.
10. Cost
In general, RAID 5 is inexpensive to implement because of the lower number of disks required.
RAID 10 costs more to install because it requires a minimum of four disks.
11. Composition
Think of RAID 5 as an array with data & parity information distributed across all disks. Imagine a long shelf divided into sections. Each row holds some data, & the other row stores parity information calculated from that data. These parity statements are similar to a basic recipe that can recreate lost data if one compartment (disk) on the shelf becomes damaged.
In RAID 10, the system is more complex. You can think of it like many small pots working together. First, the disks are divided into mirror pairs. Each pair works in a mini-array of two identical shelves. Data is written simultaneously to both shelves in the pair, providing a more accurate picture. Then, these two mirrors are used as individual units & remain patched throughout the system. Imagine that these two lenses are then placed side by side in a large storage unit, and the information is redistributed to them in groups. This allows for quick data access to the bar.
12. Advantages
RAID 5 is ideal for situations where storage efficiency is paramount & the risk of a second drive failing during a rebuild is reduced. This drive offers a great way to store large media files or records where data security is important but not mission-critical.
RAID 10 shines when data security & performance is paramount. This storage drive is perfect for mission-critical applications like database servers or financial systems where data integrity & fast access is important.
Additional Reading: Advantages and Disadvantages of RAID Levels
13. NAS Suitability
Another thing to consider when choosing is raid 5 vs raid 10 nas. RAID 5 is supported by most NAS (Network Attached Storage) devices due to its simplicity & storage efficiency.
RAID 10 may not work on all NAS devices due to its high requirement. However, higher-end NAS configurations are often helpful for users who prioritize data security.
Additional Reading: Fix ‘Raid Creation Failed’ Error on Netgear Nas
Conclusion
Remember, RAID is not an invincible shield against data loss. Permanently storing your data in a new location is crucial to ensure complete security. Regardless of which you choose, raid 5 vs 10, both offer more value than a single drive. They improve data security, improve productivity, & provide peace of mind, knowing your valuable information is securely protected.
If you found this article helpful, leave a comment below. We’d love to hear your thoughts on RAID or any other storage-related issues you’d like us to explore.
Additional Reading: Raid Server Recovery – What to Do If Your RAID Server Crashes
FAQs
1. What is RAID 10 and how does it work?
It is a storage setup that combines mirroring & striping for speed and security. Here, data is written to two multi-mirrored disks, similar to the checkered model. Requires a minimum of 4 vehicles.
2. When should you use RAID 10?
Use RAID 10 when you need better performance & data security. You can use it for important files on the server. It’s like having a safety net if the drive fails.
3. How many drives are there in RAID 5?
Usually, it uses at least 3 drives and gives good balance but has some rebuild complexity in case of failure.
Additional Reading: Go for Safe Recovery Service in Case of Raid Failure
4. Is RAID 10 or RAID 5 better for small businesses?
Small businesses often prioritize cost-effectiveness and reliability. RAID 10 offers better performance and fault tolerance, making it suitable for critical applications despite higher implementation costs.
Additional Reading: Indian Organizations Need the Help of RAID Recovery Service Providers
5. Does RAID 10 offer better write performance compared to RAID 5?
Yes, RAID 10 generally provides faster write speeds due to its mirrored configuration, which allows data to be written simultaneously to multiple disks. This results in improved performance, particularly in write-intensive applications.
Additional Reading: Misconceptions About RAID Servers