Chapter 1 of 2 | Published On
In short, a file system is the thing that tells your computer where one piece of data ends, and another begins. In short, a file system is the thing that tells your computer where one piece of data ends, and another begins.
ExFAT is the Extensible File Allocation Table, FAT32 is the latest revision to the File Allocation Table with each unit being 32 bits in size, and NTFS is the New File Transfer System.
FAT32 is very popular but is outdated, ExFAT is also popular and works seamlessly across operating systems, NTFS is the most secure but has limited inter-OS support.
Choose ExFAT if you're going to need your storage media across many operating systems, choose FAT32 if you have older generation devices, and choose NTFS if you are going to use your storage media exclusively with Windows.
The Beginning: This brings us to the question: ExFAT vs NTFS vs FAT32: what should you choose? Is one of these better in some situations than the other? If one is better, why are the others also so prevalently popular?
These, and other questions will be answered through this article. In this article, you will learn:
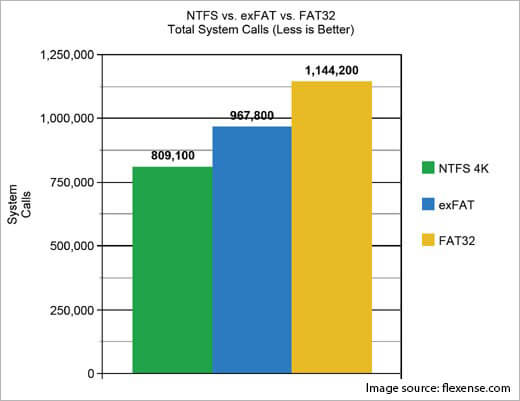
Here are the main distinctions when we talk about ExFAT vs NTFS and ExFAT vs FAT32:
1. What is a file system?
This is a short question with a long answer, but here is the essence of it: A file system is a method (coupled with a type of data structure) that controls how data is stored, retrieved, and accessed on a computer.
Think of your data like pieces of luggage, and your computer as a cargo ship. Certain pieces of luggage will have things that you need, and you cannot swap one for the other.
If you ask your computer without a file system for luggage A, the best that your computer can do is return a random piece of luggage to you.
With a file system, the computer will know exactly where each piece of luggage is, and at what times, and how long it has been there.
That is what a file system (often abbreviated to FS) does for you.
It allows the computer to distinguish between different pieces of data by telling the computer where one piece of data ends, and another begins. There are many formats, but the most popular ones are ExFAT, NTFS, FAT32, APFS (apple exclusive), and some more, but these are the most popular.
Also Read: NTFS or FAT32 Which File System to Use?
2. What is ExFAT?
In a nutshell, exFAT is a file allocation protocol (system) that was introduced by Microsoft in 2006, and which was first beta tested on internal Microsoft Corporation data hubs.
ExFAT stands for Extensible File Allocation Table, and quickly proved its prowess in the Data Management Systems (DMS) sector.
3. What is NTFS?
NTFS is an industry acronym for “New Technology File System”, it was introduced way back in ‘93, but became popular only with Windows XP.
Today, NTFS comes as standard issue with all new versions of Microsoft Windows (for all non-removable storage media attached to Windows OS devices).
It has many business and productivity pros such as multi-user controls, Access Control Lists, fault tolerance, high-grade encryption, and a whole lot more.
If you are confident that you will only write data to your storage disks from windows machines, then there is no doubt about it — NTFS is the way to go.
Also Read: Fix Ntfs.sys Error in Windows 10?
4. What is FAT32?
FAT stands for File Allocation Table, and the 32 at the back indicates that the data in this allocation table management system is stored and broken down into fragments of 32 bits each.
FAT32 was a much-needed update, designed to replace and improve upon the industry standard at the time, FAT16. As you can probably guess, FAT16 was a file allocation table that stored data in 16-bit fragments.
5. Which is the better choice overall in ExFAT vs FAT32 vs NTFS?
ExFAT is the better choice, as it is supported by more devices, file management solutions and operating systems, and supports larger files than FAT32 as well.
The main caveat to this is that FAT32 performs marginally better in certain situations, which will be detailed for you further down in the article.
NTFS, the most modern competitor of these three, is the default operating system for the majority of Windows OS machines, and for most non-removable media storage that are linked to Windows.
6. What is the difference when it comes to ExFAT Vs NTFS?
ExFAT and NTFS are remarkably similar and were introduced around the same time, but the main difference is that NTFS is read-only on all versions of macOS, but is read-only on some versions of Linux OS.
The other facet of NTFS is that it is much more secure than ExFAT as it forces EFS (Encrypted File System) technologies and protocols.
Lastly, it is worth noting that NTFS performance takes a steep dive when any of its partitions are below 400 megabytes in size.
7. What should I choose in ExFAT vs NTFS vs FAT32?
-performance.jpg)
One of the main pros of ExFAT is that it allows for the machine to have and register file sizes (of individual files) that are larger than 4 GB in totality.
On the other hand, FAT32 would handle file sizes greater than 4 gigabytes by breaking down the file into smaller chunks and fragments.
While this approach got the job done (for a very, very, long time), corruption of any sector of the drive, or any fragment of the file, the entire file would be affected, which was a major headache for users; and is one that exists even today.
Considering NTFS, if security is a concern for you at all, use NTFS, but as mentioned before, the one drawback of NTFS is that it can only read data on macOS devices, and may not work at all on Linux, depending on which version and build you are running.
Note: ExFAT vs NTFS (SSD) performance: Also if you have an internal (windows) SSD, there is little debate for ExFAT vs NTFS SSD utilities: NTFS is the clear winner in this case.
For all other intents and purposes, go with ExFAT: it is more robust and compatible than FAT32. If you do happen to be running an SSD, it is extremely unlikely that your system will not support ExFAT: if it is old enough to not support ExFAT, it is old enough to not support SSDs too.
Also Read: How To Convert Raw Partition To NTFS Without Data Loss?



